Inpatient Diabetes Guideline for Adult Non-Critically Ill Patients - NCBI Bookshelf

This guideline applies to hospitalized adult non-critically ill (non-ICU) patients in general medicine, surgical, perioperative, short-stay, and OB/GYN areas with Type 1 diabetes (T1DM), Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), stress hyperglycemia, diabetes secondary to medications, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. The objective is to promote safe, effective glycemic management in hospitalized patients targeting blood glucose (BG) to published goals while preventing hypoglycemia. Approximately 30–35% of admitted patients have diabetes. Hyperglycemia is a well-established risk factor for adverse hospital outcomes. Additionally, hypoglycemia can have deleterious consequences. Safe and effective glucose management is of paramount importance in the hospital. Additionally, a hospital admission is an opportune time to address diabetes control.

Journal Club - Early versus Late Parenteral Nutrition in

Determinants of initial insulin therapy for hospitalized patients

Medical devices, smart drug delivery, wearables and technology for

Hyperglycemic Crises: Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic
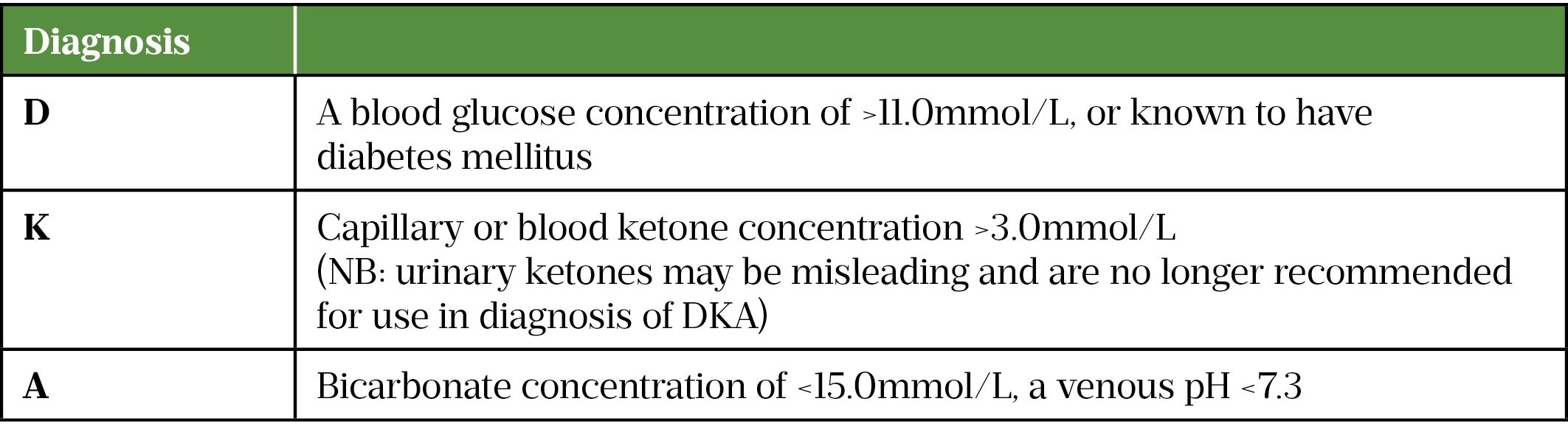
Diabetic ketoacidosis in adults: identification, diagnosis and

2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A

The Management of Type 1 Diabetes - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Using NSQIP Data to Reduce Institutional Postoperative Pneumonia

The management of type 1 diabetes in adults. A consensus report by
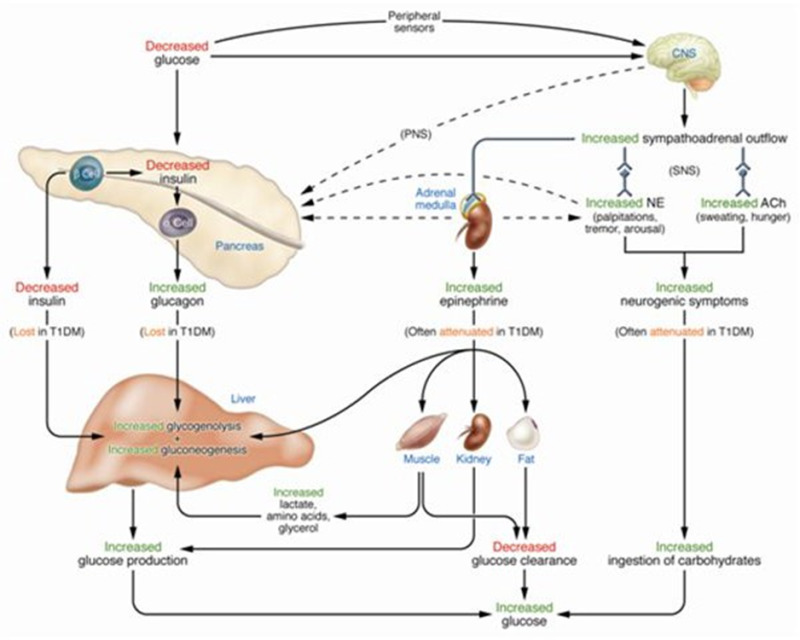
Hypoglycemia During Therapy of Diabetes - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf
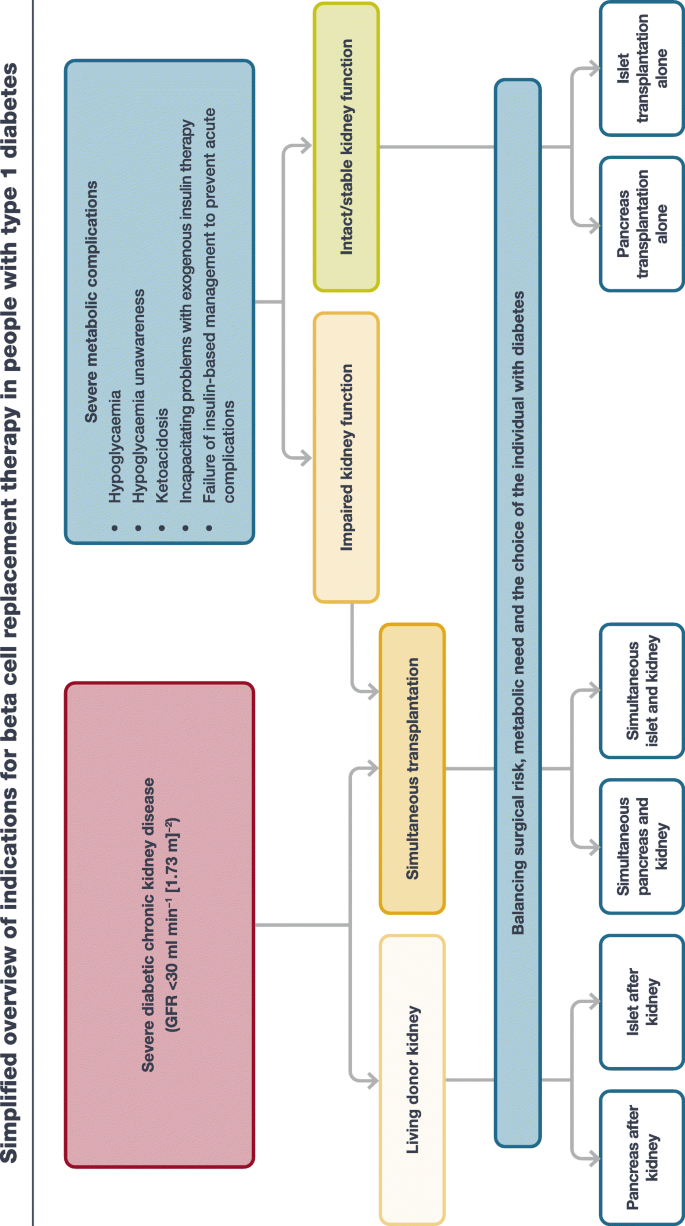
The management of type 1 diabetes in adults. A consensus report by







